lncRNA and circRNA expression profiles in the hippocampus of Aβ25‑35‑induced AD mice treated with Tripterygium glycoside
Aβ 25‑35 ‑诱导的阿尔茨海默病小鼠海马中 Tripterygium glycoside 处理的 lncRNA 和 circRNA 表达谱
- PMID: 37602300
- PMCID: PMC10433443
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2023.12125
lncRNA and circRNA expression profiles in the hippocampus of Aβ25‑35‑induced AD mice treated with Tripterygium glycoside
Abstract 摘要
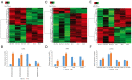
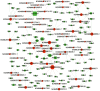
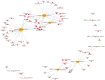
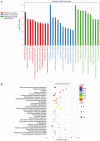
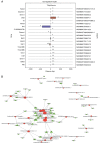
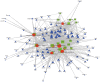
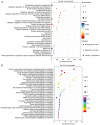
Tripterygium glycosides (TG) have been reported to ameliorate Alzheimer's disease (AD), although the mechanism involved remains to be determined. In the present study, the lncRNA and circRNA expression profiles of an AD mouse model treated with TG were assessed using microarrays. lncRNAs, mRNAs, and circRNAs in the hippocampi of 3 AD+normal saline (NS) mice and 3 AD+TG mice were detected using microarrays. The most differentially expressed lncRNAs, mRNAs, and circRNAs were screened between the AD+NS and AD+TG groups. The differentially expressed lncRNAs and circRNAs were analyzed using GO enrichment and KEGG analyses. Co-expression analysis of lncRNAs, circRNAs, and mRNAs was performed by calculating the correlation coefficients. Protein-protein interaction (PPI) network analysis was performed on mRNAs using STRING. The lncRNA-target-transcription factor (TF) network was analyzed using the Network software. In total, 661 lncRNAs, 64 circRNAs, and 503 mRNAs were found to be differentially expressed in AD mice treated with TG. Pou4f1, Egr2, Mag, and Nr4a1 were the hub genes in the PPI network. The KEGG results showed that the mRNAs that were co-expressed with lncRNAs were enriched in the TNF, PI3K-Akt, and Wnt signaling pathways. LncRNA-target-TF network analysis indicated that TFs, including Cebpa, Zic2, and Rxra, were the most likely to regulate the detected lncRNAs. The circRNA-miRNA interaction network indicated that 275 miRNAs may bind to the 64 circRNAs. In conclusion, these findings provide a novel perspective on AD pathogenesis, and the detected lncRNAs, mRNAs, and circRNAs may serve as novel therapeutic targets for the management of AD.
三萜苷(TG)已被报道可以改善阿尔茨海默病(AD),尽管相关机制尚待确定。在本研究中,使用微阵列评估了 TG 处理的 AD 小鼠模型的 lncRNA 和 circRNA 表达谱。通过微阵列检测了 3 只 AD+生理盐水(NS)小鼠和 3 只 AD+TG 小鼠海马中的 lncRNA、mRNA 和 circRNA。筛选出 AD+NS 组和 AD+TG 组之间表达差异最大的 lncRNA、mRNA 和 circRNA。使用 GO 富集和 KEGG 分析对差异表达的 lncRNA 和 circRNA 进行了分析。通过计算相关系数对 lncRNA、circRNA 和 mRNA 进行了共表达分析。使用 STRING 对 mRNA 进行了蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用(PPI)网络分析。使用 Network 软件分析了 lncRNA-靶标-转录因子(TF)网络。总共发现 661 个 lncRNA、64 个 circRNA 和 503 个 mRNA 在 TG 处理的 AD 小鼠中表达差异。Pou4f1、Egr2、Mag 和 Nr4a1 是 PPI 网络中的核心基因。 KEGG 结果显示,与 lncRNA 共同表达的 mRNA 在 TNF、PI3K-Akt 和 Wnt 信号通路中富集。LncRNA-靶标-TF 网络分析表明,包括 Cebpa、Zic2 和 Rxra 在内的 TF 最有可能调控检测到的 lncRNA。circRNA-miRNA 相互作用网络表明,275 个 miRNA 可能与 64 个 circRNA 结合。总之,这些发现为 AD 发病机制提供了新的视角,检测到的 lncRNA、mRNA 和 circRNA 可能作为 AD 管理的新治疗靶点。
Keywords:
Alzheimer's disease; Tripterygium glycoside; circRNA; lncRNA.
关键词:阿尔茨海默病;雷公藤苷;circRNA;lncRNA。
Copyright: © Tang et al.
版权:© Tang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
利益冲突声明
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
作者声明他们没有竞争利益。
Figures 数字

Similar articles
-
In-depth analyses of lncRNA and circRNA expression in the hippocampus of LPS-induced AD mice by Byu d Mar 25.Neuroreport. 2024 Jan 3;35(1):49-60. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000001977. Epub 2023 Nov 25. Neuroreport. 2024. PMID: 38051653 Free PMC article.
-
lncRNA-Associated Competitive Endogenous RNA Regulatory Network in an Aβ25-35-Induced AD Mouse Model Treated with Tripterygium Glycoside.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2021 May 19;17:1531-1541. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S310271. eCollection 2021. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2021. PMID: 34040378 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated analysis of lncRNA/circRNA-miRNA-mRNA in the proliferative phase of liver regeneration in mice with liver fibrosis.BMC Genomics. 2023 Jul 24;24(1):417. doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09478-z. BMC Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37488484 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of altered exosomal microRNAs and mRNAs in Alzheimer's disease.Ageing Res Rev. 2022 Jan;73:101497. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2021.101497. Epub 2021 Oct 26. Ageing Res Rev. 2022. PMID: 34710587 Review.
-
Gut microbiota-lncRNA/circRNA crosstalk: implications for different diseases.Crit Rev Microbiol. 2024 Jul 5:1-15. doi: 10.1080/1040841X.2024.2375516. Online ahead of print. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38967384 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the causal relationships between type 2 diabetes and neurological disorders using a Mendelian randomization strategy.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Nov 15;103(46):e40412. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040412. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39560586 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the Network regulatory mechanism of ncRNAs on the Ferroptosis Pathway: Implications for Preeclampsia.Int J Womens Health. 2024 Sep 30;16:1633-1651. doi: 10.2147/IJWH.S485653. eCollection 2024. Int J Womens Health. 2024. PMID: 39372667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the Regulatory Landscape of Dementia: Insights from Non-Coding RNAs.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 4;25(11):6190. doi: 10.3390/ijms25116190. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892378 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory roles of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) methylation in RNA processing and non-communicable diseases.Cancer Gene Ther. 2024 Oct;31(10):1439-1453. doi: 10.1038/s41417-024-00789-1. Epub 2024 Jun 5. Cancer Gene Ther. 2024. PMID: 38839892 Review.
-
Autophagy-associated non-coding RNAs: Unraveling their impact on Parkinson's disease pathogenesis.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 May;30(5):e14763. doi: 10.1111/cns.14763. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 38790149 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wenk GL. Neuropathologic changes in Alzheimer's disease. J Clin Psychiatry. 2003;64:7–10. - PubMed
-
- Wei M, Liu Y, Pi Z, Li S, Hu M, He Y, Yue K, Liu T, Liu Z, Song F, Liu Z. Systematically characterize the anti-Alzheimer's disease mechanism of lignans from S. chinensis based on in-vivo ingredient analysis and target-network pharmacology strategy by UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS. Molecules. 2019;24(1203) doi: 10.3390/molecules24071203. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
